Stock Market Basics: Get ready to dive into the fundamentals of the stock market with this engaging overview that will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the financial world like a pro. From understanding what the stock market is all about to the key players in the ecosystem, this introduction sets the stage for an exciting journey into the world of investing.
Whether you’re a newbie looking to dip your toes into the market or a seasoned investor seeking to brush up on the basics, this guide is your go-to resource for demystifying the complexities of stock trading and unlocking the secrets to successful investing.
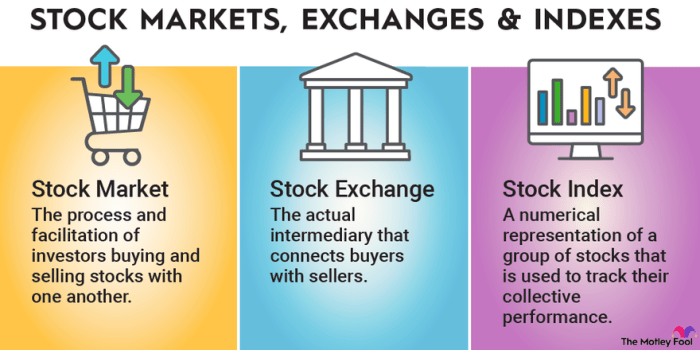
Overview of Stock Market Basics
Investing in the stock market can be a lucrative way to grow your wealth over time. However, before diving in, it’s crucial to understand the fundamentals of how the stock market operates. Let’s break it down.
What is the Stock Market?
The stock market is a platform where individuals and institutions can buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. These shares represent ownership in the company and are traded on stock exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or the NASDAQ.
Importance of Understanding Stock Market Basics
Having a solid grasp of stock market basics is essential for investors to make informed decisions. By understanding concepts like stock prices, market trends, and risk management, investors can navigate the market with more confidence and potentially increase their chances of success.
Key Players in the Stock Market Ecosystem
- Investors: Individuals or institutions who buy and sell stocks.
- Companies: Publicly traded businesses that issue shares to raise capital.
- Stockbrokers: Professionals who facilitate the buying and selling of stocks on behalf of investors.
- Market Analysts: Experts who analyze market trends and provide insights to investors.
- Regulators: Government agencies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) that oversee and regulate the stock market.
Types of Stocks

When it comes to investing in the stock market, there are different types of stocks available for investors to choose from. Two common types are common stocks and preferred stocks, each with its own set of characteristics and risks.
Common Stocks vs. Preferred Stocks
Common stocks are the most common type of stocks that investors purchase. When you buy common stock, you are essentially buying a share of ownership in the company. This type of stock typically comes with voting rights at shareholder meetings and the potential to receive dividends.
On the other hand, preferred stocks are a type of stock that has a higher claim on the company’s assets and earnings compared to common stocks. Preferred stockholders receive dividends before common stockholders and have a fixed dividend rate. However, preferred stockholders usually do not have voting rights.
Benefits and Risks
- Common stocks offer the potential for higher returns through capital appreciation and dividends. However, they also come with higher risk as their value can fluctuate based on market conditions.
- Preferred stocks, on the other hand, provide a more stable income stream through fixed dividends. They are less volatile compared to common stocks but may not offer as much potential for capital appreciation.
- Investing in common stocks can provide investors with voting rights and the potential for higher returns, but it also comes with the risk of losing money if the company’s stock price declines.
- Preferred stocks are less risky than common stocks in terms of dividend payments and claim on assets. However, they may not offer as much growth potential as common stocks.
Stock Market Indices
Stock market indices are a way to measure and track the performance of a group of stocks representing a particular market or sector. They provide investors with a snapshot of how the overall market or specific sectors are performing.
Popular Stock Market Indices
- The S&P 500: This index tracks the performance of 500 large-cap companies listed on the stock exchanges in the United States. It is widely regarded as a barometer of the overall health of the U.S. stock market.
- Dow Jones Industrial Average: Also known as the Dow, this index consists of 30 large publicly traded companies in the United States. It is one of the oldest and most widely followed stock market indices.
- NASDAQ Composite: This index includes over 2,500 stocks listed on the NASDAQ stock exchange. It is known for its heavy representation of technology and internet-related companies.
Stock market indices are calculated using different methodologies, such as market capitalization weighting, price weighting, or equal weighting. These methodologies determine the impact of each stock on the index’s performance.
Significance to Investors
- Investors use stock market indices to gauge the overall market sentiment and trend. They can compare their portfolio performance against these indices to assess how well they are doing.
- Stock market indices serve as benchmarks for mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) to measure their performance against the broader market.
- Indices like the S&P 500 are often used as indicators of the economy’s health and can influence investor confidence and behavior.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis is a method used by investors to evaluate the intrinsic value of a stock. It involves examining various financial metrics and economic factors to determine whether a stock is overvalued, undervalued, or fairly priced.
Key Financial Metrics
- The P/E ratio (Price-to-Earnings ratio) is a valuation metric that compares a company’s current share price to its earnings per share (EPS). A high P/E ratio may indicate an overvalued stock, while a low P/E ratio could suggest an undervalued stock.
- The EPS (Earnings Per Share) is a measure of a company’s profitability. It is calculated by dividing a company’s net income by the number of outstanding shares. A higher EPS typically indicates a more profitable company.
- The ROE (Return on Equity) ratio measures a company’s profitability by evaluating how effectively it is using shareholder equity to generate profits. A higher ROE is usually preferred as it signifies efficient use of capital.
Importance of Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis helps investors make informed decisions by providing a deeper understanding of a company’s financial health, management quality, industry trends, and overall market conditions. By analyzing key financial metrics like P/E ratio, EPS, and ROE, investors can assess the value and growth potential of a stock, thereby reducing the risk of making uninformed investment choices.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves analyzing historical price and volume data to predict future price movements. Unlike fundamental analysis, which focuses on a company’s financial health and intrinsic value, technical analysis relies solely on past market data.
Common Technical Analysis Tools
- Moving Averages: Moving averages help smooth out price data to identify trends over time. The most common types are simple moving averages (SMA) and exponential moving averages (EMA).
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. It is used to determine overbought or oversold conditions.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price. It is used to identify changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend.
Examples of Technical Analysis in Predicting Stock Price Movements
For example, if a stock’s price breaks above a key resistance level after forming a bullish chart pattern, such as a cup and handle, technical analysts may interpret this as a signal to buy the stock.
Another example is when the MACD line crosses above the signal line, indicating a potential uptrend in the stock’s price.
Investing Strategies: Stock Market Basics
When it comes to investing in the stock market, having a solid strategy is key to achieving your financial goals. There are several popular investing strategies that investors can consider, each with its own set of principles and applications. Let’s explore some of the most common strategies and provide tips for beginners on choosing the right one.
Value Investing
- Value investing involves looking for stocks that are undervalued by the market.
- Investors using this strategy focus on buying stocks at a price below their intrinsic value, with the belief that the market will eventually recognize the true worth of the company.
- Key principle: Buy low, sell high.
Growth Investing, Stock Market Basics
- Growth investing is centered around investing in companies that are expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to the overall market.
- Investors following this strategy prioritize companies with strong growth potential, even if the current stock price may seem high.
- Key principle: Focus on future growth prospects rather than current valuation.
Dividend Investing
- Dividend investing involves investing in companies that regularly pay dividends to their shareholders.
- Investors who prefer this strategy seek stable and reliable income from dividend payments, in addition to potential capital appreciation.
- Key principle: Generate income through dividend payments while benefiting from potential stock price appreciation.
For beginners, it’s important to assess your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline before choosing an investing strategy. Consider seeking advice from financial professionals or doing thorough research to ensure the strategy aligns with your objectives.
Risks in the Stock Market
When it comes to investing in the stock market, there are several risks that investors need to be aware of. These risks can impact the value of their investments and potentially lead to losses if not managed properly.
Market Volatility
Market volatility refers to the rapid and unpredictable price movements in the stock market. This can be caused by various factors such as economic events, political instability, or even investor sentiment. High volatility can lead to significant fluctuations in stock prices, making it challenging to predict market movements accurately.
Company-Specific Risks
Company-specific risks are risks that are unique to a particular company. These risks can include poor management decisions, product recalls, or legal issues. Investing in a single company’s stock exposes investors to the specific risks associated with that company, which can impact the stock price significantly.
External Factors
External factors such as interest rates, inflation, and geopolitical events can also impact stock prices. Changes in these external factors can influence investor behavior and market sentiment, leading to fluctuations in stock prices. It is essential for investors to stay informed about these external factors and their potential impact on the stock market.
Strategies for Managing Risks
To manage and mitigate risks when investing in stocks, investors can employ various strategies. Diversification, for example, involves spreading investments across different asset classes and industries to reduce exposure to any single risk. Setting stop-loss orders can help limit potential losses by automatically selling a stock if it reaches a predetermined price. Additionally, conducting thorough research and analysis before making investment decisions can help investors make more informed choices and mitigate risks effectively.






